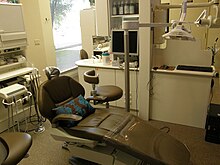
Dentistry usually encompasses very important practices related to the oral cavity. Oral diseases are major public health problems due to their high incidence and prevalence across the globe with the disadvantaged affected more than other socio-economic groups. Although modern day dental practice centres around prevention, many treatments or interventions are still needed. The majority of dental treatments are carried out to prevent or treat the two most common oral diseases which are dental caries (tooth decay) and periodontal disease (gum disease or pyorrhea). Common treatments involve the restoration of teeth as a treatment for dental caries (fillings), extraction or surgical removal of teeth which cannot be restored, scaling of teeth to treat periodontal problems and endodontic root canal treatment to treat abscessed teeth. All dentists train for around 4 or 5 years at University and qualify as a ’dental surgeon’. By nature of their general training they can carry out the majority of dental treatments such as restorative (fillings, crowns, bridges), prosthetic (dentures), endodontic (root canal) therapy,periodontal (gum) therapy, and exodontia (extraction of teeth), as well as performing examinations, radiographs (x-rays) and diagnosis. Dentists can also prescribe certain medications such as antibiotics, fluorides, and sedatives but they are not able to prescribe the full range that physicians can. Dentists need to take additional qualifications or training to carry out more complex treatments such as sedation, oral and maxillofacial surgery, and implants. Whilst the majority of oral diseases are unique and self limiting, some can indicate poor general health,tumours,blood dyscrasias and abnormalities including genetic problems 
Sagittal section of a tooth 
Farmer at the dentist, Johann Liss, c. 1616-17. Nursing is a healthcare profession focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life from conception to death. Nurses work in a large variety of specialties where they work independently and as part of a team to assess, plan, implement and evaluate care. Nursing Science is a field of knowledge based on the contributions of nursing scientist through peer reviewed scholarly journals and evidenced-based practice See also: Category:Nurses and Category:Nursing museums

Florence Nightingale, "Lady with the Lamp", a pioneer of modern nursing In fifth century BC, Hippocrates was one of the first people in the world to study healthcare, earning him the title of "the father of modern medicine". Jesus Christ also taught that sick people should be cared for; in around 370 AD, one of the first Christian hospitals in the world was built in Cappadocia. Western European concepts of nursing were first practised by male Catholic monks who provided for the sick and ill during the Dark Ages of Europe. During 17th century Europe, nursing care was provided by men and women serving punishment. It was often associated with prostitutes and other female criminals serving time. They had a reputation for being drunk and obnoxious, a view amplified by the doctors of the time to make themselves seem more important and able. It was not until Florence Nightingale, a well-educated woman from a middle class family, became a nurse and improved it drastically that people began to accept nursing as a respectable profession. Other aspects also helped in the acceptance of nursing. In 1853 Theodore Fliedner set up a hospital where the nurses he employed had to be of good nature. Many people were impressed with this facility, and because of it, the British Institute of Nursing Sisters was set up. Prior to the foundation of modern nursing, nuns and the military often provided nursing-like services. The religious and military roots of modern nursing remain in evidence today in many countries, for example in the United Kingdom, senior female nurses are known as sisters. It was during time of war that a significant development in nursing history arose when English nurse Florence Nightingale, working to improve conditions of soldiers in the Crimean War, laid the foundation stone of professional nursing with the principles summarised in the book Notes on Nursing. Other important nurses in the development of the profession include: Mary Seacole, who also worked as a nurse in the Crimea; Agnes Elizabeth Jones and Linda Richards, who established quality nursing schools in the USA and Japan, and Linda Richards who was officially America’s first professionally trained nurse, graduating in 1873 from the New England Hospital for Women and Children in Boston. New Zealand was the first country to regulate nurses nationally, with adoption of the Nurses Registration Act on the 12 September 1901. It was here in New Zealand that Ellen Dougherty became the first registered nurse. North Carolina was the first state in the United States to pass a nursing licensure law in 1903. Nurses have experienced difficulty with the hierarchy in medicine that has resulted in an impression that nurses’ primary purpose is to follow the direction of physicians. This tendency is certainly not observed in Nightingale’s Notes on Nursing, where the physicians are mentioned relatively infrequently, and often in critical tonesâ€â€particularly relating to bedside manner. The modern era has seen the development of nursing degrees and nursing has numerous journals to broaden the knowledge base of the profession. Nurses are often in key management roles within health services and hold research posts at universities A laboratory (informally, lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. The title of laboratory is also used for certain other facilities where the processes or equipment used are similar to those in scientific laboratories. These notably include:
In recent years government and private centers for innovation in learning, leadership and organization have adopted "lab" in their name to emphasize the experimental and research-oriented nature of their work. Scientific laboratories can be found in schools and universities, in industry, in government or military facilities, and even aboard ships and spacecraft. A laboratory might offer work space for just one to more than thirty researchers depending on its size and purpose 
Modern biochemistry laboratory at the University of Cologne 
Chemistry laboratory of the 18th century, of the sort used by Antoine Lavoisier and his contemporaries
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : Wholesale of medical and dental instruments, orthopedic nursing and laboratory supplies |
|||||||||||||||